Ensuring Comparability Across Laboratories with Cequator’s Peer Grouping
In a clinical external quality assurance (EQA) program, peer grouping is an option to ensure better-suited comparisons between laboratories. A peer group consists of laboratories that use the same or similar analytical methods, instruments, reagent systems, etc. Peer groups are helpful to identify systematic issues—such as due to instrument make, calibration drift or reagent issues—and for alleviating issues related to the non-commutability of samples (Tanasković et al., 2016).
Without peer grouping, comparisons between different laboratories can be misleading. Variations in results might stem from differences in methodology rather than from the lab’s actual performance. The Youden plot below shows exemplary results showing Laboratory scores that form two peer groups in an EQA program.
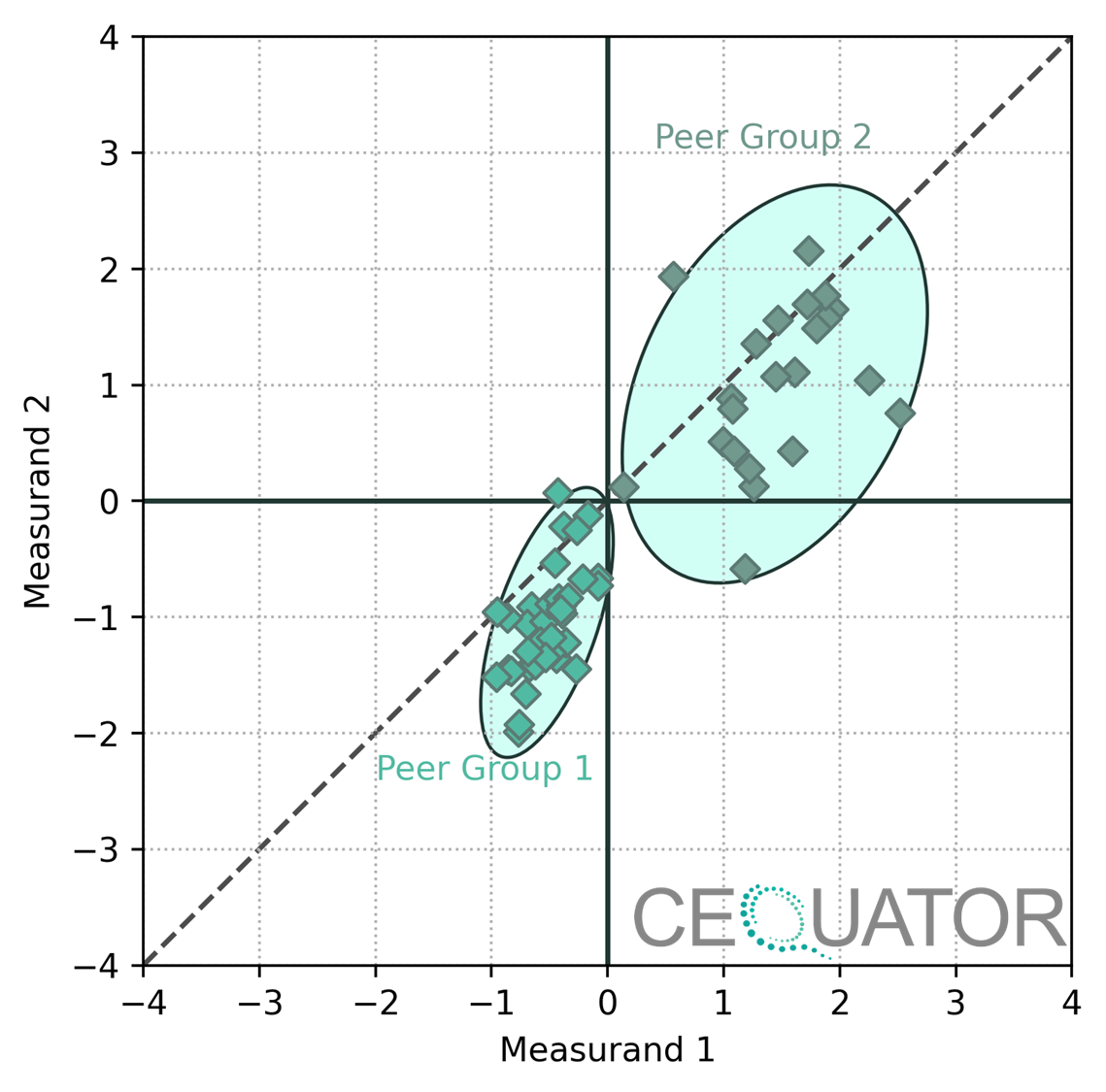
Youden plot showing two groups of laboratories
With Cequator, EQA organizers can easily create peer groups with as few as six labs per group. With a guided approach, you are in control with how you define the peer groups, i.e., same instrument type, measurement method, reagents, method, instrument manufacturer, etc. The robust algorithm utilized for performance evaluation is the Q/Hampel method as described in ISO 13528:2022. This robust statistical method aids in accurate assessment of a lab’s performance for the specific measurands within the peer group. Additionally, Cequator’s batch processing feature allows users to apply the same peer grouping methodology across all measurands and test samples with just one click!
In a nutshell, the key advantages of peer grouping are:
- Meaningful Comparisons: Peer grouping based on same instrument, method, etc. ensures relevant and accurate evaluation of labs following similar workflows.
- Error Detection: Deviations from the peer group mean can indicate potential reagent issues, instrument errors, or process deviations for the given lab, allowing timely investigation and corrective action.
Peer Group analysis in Cequator:

Setting up workflow stages: Cequator allows you to set up workflow stages with various procedural steps. For example, you can create peer groups for one measurand based on a specific procedural step, such as the type of instrument used, and create separate peer groups for another measurand based on a different procedural step, like the method or extraction kit used.
Below is an example of how a data entry with two workflow stages ("Preparation" and "Analysis") with two procedural steps each will look like in Cequator.
Setting up Workflow stages in Cequator
- Peer group initialization: You can group your participants' results according to the workflow stages in your scheme. The video below demonstrates the peer group initialization by instrument for the analyte "Basophils" in "Sample A."
Peer group customization: You can merge different peer groups based on workflow stage similarities (as shown in the video, where all Mindray and Sysmex instruments are combined). Additionally, you can easily remove groups with no participants.
Batch processing: Grouping several labs based on different factors, measurands, and test samples can be complex and time-consuming. Cequator’s batch processing capability streamlines this process by applying peer grouping methodologies efficiently. This feature not only saves time but also minimizes errors that can occur with manual processing, making EQA evaluations more efficient and user-friendly.
Analysis of EQA programs with peer grouping should no longer be a pain point for you with Cequator. By ensuring relevant comparisons, detecting errors, and streamlining processes, Cequator empowers you in achieving and maintaining high standards of quality in your EQA study.
References
Tanasković, J. V., Coucke, W., Krleža, J. L., & Rodriguez, J. V. (2016). Peer groups splitting in Croatian EQA scheme: a trade-off between homogeneity and sample size number. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM), 55(4). https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2016-0284
International Organization for Standardization. (2022). ISO 13528:2022: Statistical methods for use in proficiency testing by interlaboratory comparison. ISO https://www.iso.org/standard/76484.html
